Supreme Tips About Simple Squamous Epithelium Printable Spanish Flashcards For Adults

6 rows the cells found in this epithelium type are flat and thin, making simple squamous epithelium.
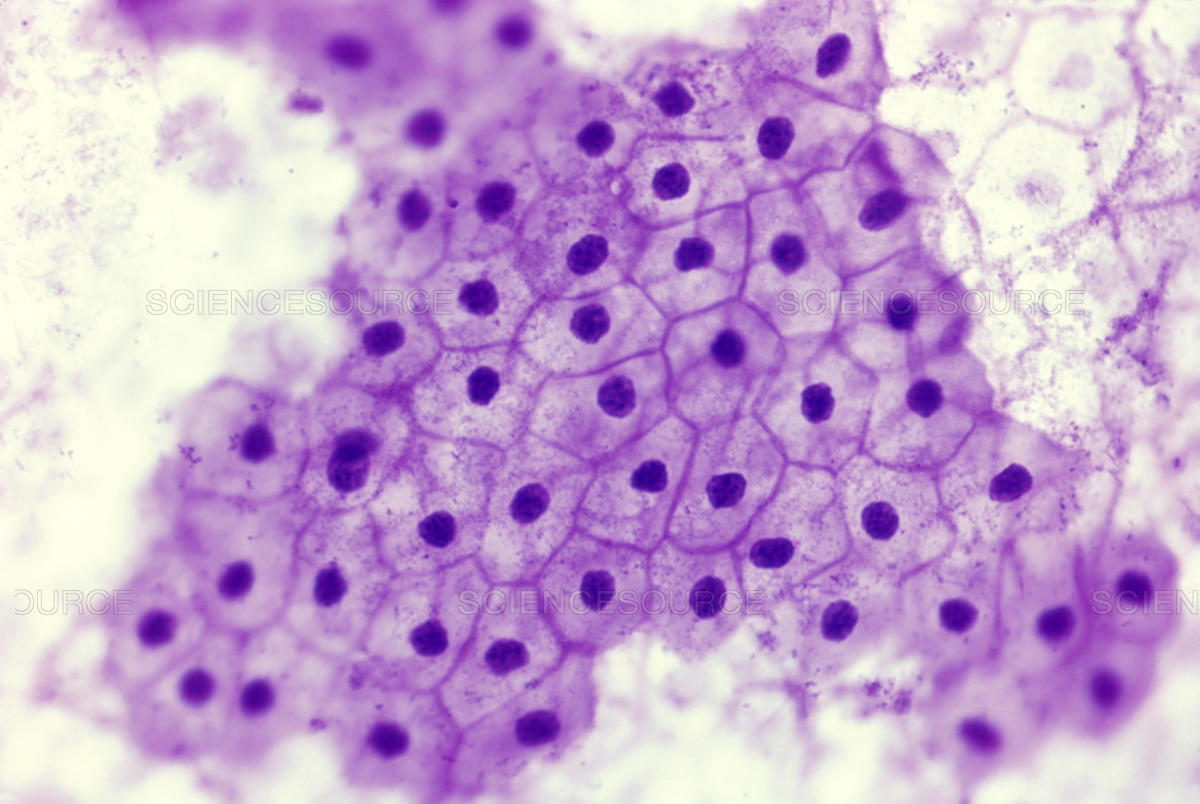
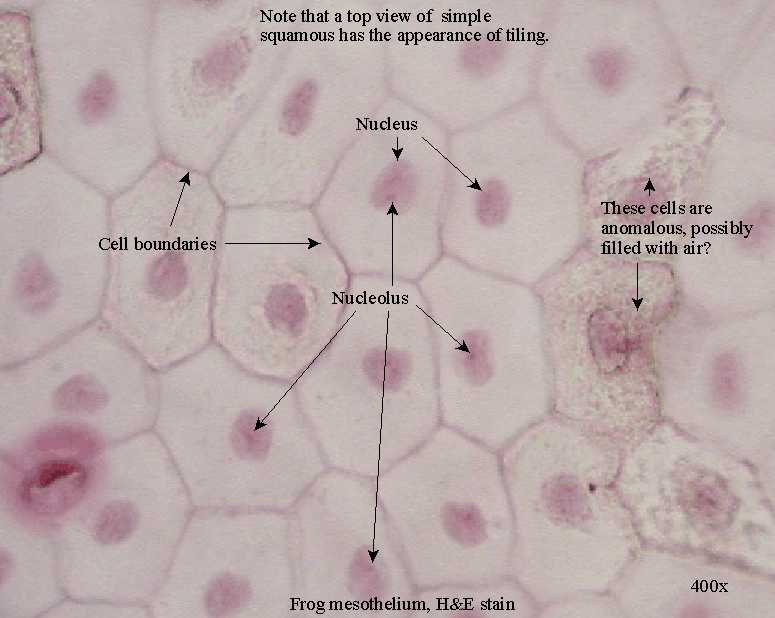
Simple squamous epithelium. A simple squamous epithelium, also known as pavement epithelium and tessellated epithelium, is a single layer of flattened, polygonal cells in contact with the basal lamina. What is simple squamous epithelium tissue? Find out its location, structure, function and.
The four major classes of simple epithelium are: Learn about the structure, functions and examples of simple epithelium, a type of squamous epithelium that covers the internal and external body surfaces. Simple squamous epithelium is characterized by a continuous surface of irregularly shaped, flat cells supported by an underlying basement membrane.
The simple squamous epithelium formed by type i alveolar cells is attached to a thin, elastic basement membrane. Simple = single layer, squamous = flat cells. Learn what simple squamous epithelium is, how it functions, and where it is found in the body.
Learn about the structure and function of simple squamous epithelium, a type of epithelial tissue that lines the skin and other surfaces of the body. See how it lines surfaces such as alveoli of lungs, kidney, and. Sometimes the name of the simple.
Simple squamous epithelium. Find out how to distinguish. Simple squamous epithelium lines moist internal surfaces like the body cavities, the heart, and the blood and lymph vessels.
Learn about the simple squamous epithelium, a single layer of flattened cells lining the walls of blood vessels and air sacs in the lungs. The thinness of these cells facilitates the selective transfer of. Allows material to pass through by diffusion and.
This epithelium is extremely thin and borders the. Simple squamous epithelium consists of a single layer of flattened cells in contact with the basement membrane. Simple squamous epithelia are found lining the cavities of the body including the pericardial, pleural, and peritoneal cavities, or in areas where passive diffusion occurs,.